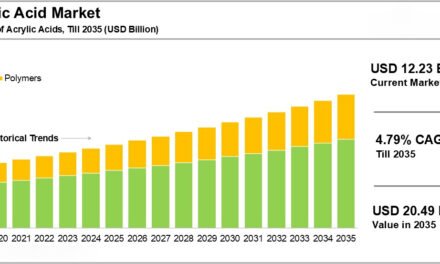
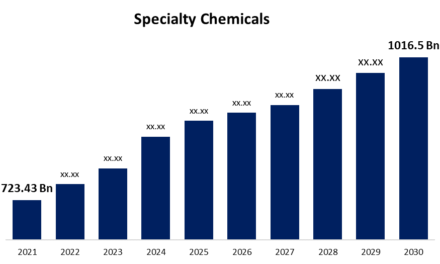
The Role of Regulations in the Acrylic Industry
Regulations play a crucial role in shaping the acrylic manufacturing industry, influencing product formulations, sustainability efforts, environmental impact, and workplace safety. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide impose stringent guidelines to address pollution, health risks, and sustainability concerns. Here are the key ways in which regulations affect the industry:
1. Environmental Regulations and Emission Controls
Impact:
- Acrylic production often involves volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), leading to stricter environmental laws.
- Manufacturers must reduce emissions from production processes, especially in the synthesis of methyl methacrylate (MMA), a key acrylic monomer.
- Laws such as the Clean Air Act (USA) and EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) impose strict limits on harmful emissions.
Industry Response:
- Development of low-VOC and water-based acrylic formulations in coatings, paints, and adhesives.
- Adoption of closed-loop manufacturing and improved filtration systems to reduce emissions.
- Investment in bio-based and recyclable acrylics to comply with sustainability mandates.
2. Waste Management and Recycling Policies
Impact:
- Acrylics are non-biodegradable, creating significant waste challenges, particularly in packaging and construction materials.
- Regulations encourage recycling and circular economy practices to minimize landfill waste.
- Countries with extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies require manufacturers to manage acrylic waste disposal.
Industry Response:
- Introduction of chemical recycling techniques, including depolymerization, to convert acrylic waste into reusable monomers.
- Growth in mechanical recycling initiatives to enhance post-consumer acrylic recovery.
- Compliance with regulations such as the European Green Deal and China’s Plastic Waste Reduction Policies.
3. Occupational Safety and Worker Protection
Impact:
- Acrylic manufacturing involves exposure to toxic chemicals and flammable materials, leading to strict workplace safety laws.
- Agencies like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration – USA) and HSE (Health and Safety Executive – UK) regulate exposure limits for MMA and other hazardous substances.
Industry Response:
- Implementation of protective gear, improved ventilation, and automated systems to reduce worker exposure.
- Adoption of safer alternatives, such as green solvents and non-toxic catalysts, to improve workplace conditions.
4. Consumer Product Regulations and Safety Standards
Impact:
- Acrylic products used in food packaging, medical devices, and children’s toys must comply with safety and toxicity regulations.
- Certifications like FDA (Food and Drug Administration – USA) and EU Food Contact Materials Regulation ensure acrylic materials are BPA-free, non-toxic, and safe for consumers.
Industry Response:
- Development of phthalate-free and food-safe acrylic formulations for packaging and medical applications.
- Increased use of biocompatible acrylics in healthcare and dental products to meet safety standards.
5. Sustainability and Green Chemistry Compliance
Impact:
- Global regulations are pushing the industry towards sustainable materials and carbon neutrality.
- The Paris Agreement and Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directives (CSRD) require manufacturers to track and reduce their carbon footprint.
Industry Response:
- Investment in bio-based MMA production using renewable resources.
- Adoption of green chemistry principles, such as solvent-free and low-energy polymerization processes.
- Companies obtaining eco-label certifications, including LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems).
6. Trade Regulations and Market Compliance
Impact:
- Import/export restrictions on hazardous materials impact global supply chains.
- Trade agreements and tariffs affect raw material availability and pricing.
- Certification requirements such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances – EU) dictate compliance for electronics and automotive acrylic components.
Industry Response:
- Diversification of supply chains to reduce dependency on specific markets.
- Innovation in substitute materials that meet multiple regional compliance standards.