The potential for bio-based substitutes in petrochemicals is significant, driven by environmental, economic, and technological factors. Here’s an overview:
1. Environmental Benefits
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Bio-based substitutes can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil-based products.
- Renewable Resources: They are derived from renewable raw materials like plant oils, agricultural waste, or algae, reducing reliance on finite petroleum resources.
- Waste Utilization: Agricultural residues and other waste streams can be transformed into valuable bio-chemicals.
2. Market Drivers
- Regulatory Push: Governments worldwide are encouraging sustainable practices and imposing stricter regulations on carbon emissions and plastic waste.
- Consumer Demand: Increasing awareness among consumers for eco-friendly products drives the demand for bio-based alternatives.
- Corporate Sustainability Goals: Companies are incorporating bio-based materials to align with sustainability targets.
3. Application Potential
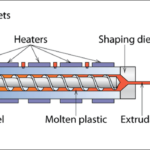
- Bio-plastics: Substitutes for traditional plastics, used in packaging, automotive, and electronics.
- Bio-fuels: Alternatives like bioethanol and biodiesel replace petrochemical-based fuels.
- Specialty Chemicals: Bio-based adhesives, coatings, and surfactants cater to diverse industrial applications.
- Polymers: Bio-polyethylene and bio-polypropylene are emerging as viable substitutes for conventional polymers.
4. Challenges to Overcome
- Cost Competitiveness: Bio-based products are often costlier than petrochemicals, making large-scale adoption challenging.
- Feedstock Availability: Dependence on agricultural inputs can strain food resources or be affected by climate variability.
- Technology Maturity: Advanced technologies are required to efficiently convert bio-feedstocks into high-performance substitutes.
5. Future Potential
- Innovation in Bio-refining: Improved bio-refineries can increase yields and diversify the range of products.
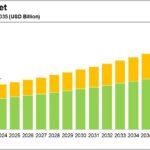
- Scaling Production: Larger-scale operations can help reduce costs and meet growing demand.
- Integration with Circular Economy: Bio-based chemicals combined with recycling technologies can drive a sustainable chemical ecosystem.