The future of excipients in drug delivery systems is evolving rapidly, driven by innovation and the need for more effective, targeted, and patient-friendly therapies. Here’s what to expect:
1. Functional Excipients
- Enhanced Solubility: Excipients that improve the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs, such as cyclodextrins and lipid-based carriers.
- Controlled Release: Smart polymers and hydrogels that enable sustained, controlled, or targeted drug release over time.
2. Biocompatibility and Safety
- Development of excipients with improved biocompatibility and reduced toxicity profiles to meet stricter regulatory requirements.
3. Targeted Drug Delivery
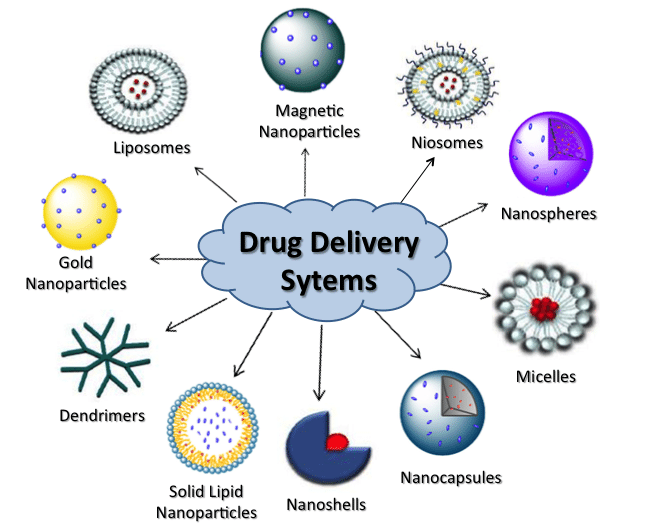
- Excipients designed for site-specific delivery, such as nanoparticles or liposomes, enhancing drug effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
4. Personalized Medicine
- Customizable excipients tailored to individual patient needs, such as specific dissolution rates or delivery mechanisms for unique drug formulations.
5. Excipients for Biologics
- Advances in excipients that stabilize and deliver sensitive biological drugs like peptides, proteins, and monoclonal antibodies.
6. Multi-Functional Excipients
- Excipients that combine multiple roles, such as acting as fillers, stabilizers, and enhancers, simplifying formulations and reducing costs.
7. Green Excipients
- Development of sustainable and environmentally friendly excipients derived from natural or renewable sources.
8. Nanotechnology Integration
- Use of nano-excipients for precise drug targeting, improved bioavailability, and enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
9. 3D Printing of Drug Formulations
- Excipients compatible with 3D printing technology, enabling on-demand production of complex drug delivery systems.
10. Enhanced Stability
- Excipients that increase the stability of drugs, especially those sensitive to heat, light, or moisture.
11. Patient-Centric Formulations
- Taste-masking agents, disintegrants for fast-dissolving tablets, and excipients for chewable or liquid formulations to improve patient compliance.
12. Regulatory Harmonization
- Standardization of expedient quality and safety assessments globally to facilitate innovation and market entry.