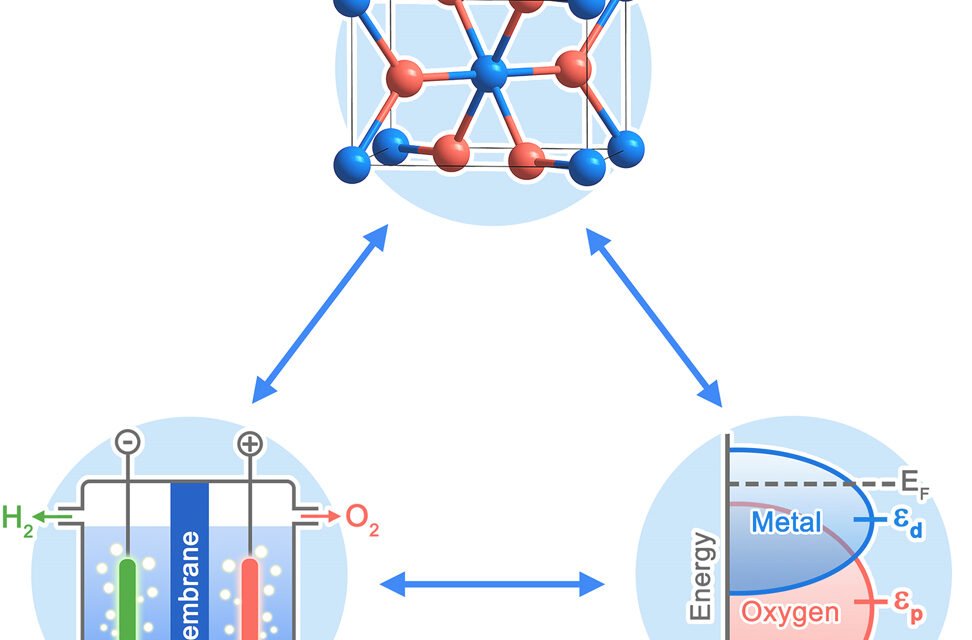
The future of catalysts in chemical manufacturing is poised for transformative advancements, driven by the need for sustainability, efficiency, and economic growth. Catalysts, critical to reducing energy consumption and enhancing reaction rates, are undergoing a revolution with the development of nanotechnology, AI-driven design, and bio-inspired approaches. Emerging trends include the creation of highly selective catalysts that minimize byproducts, thus reducing waste and environmental impact. Additionally, researchers are focusing on renewable catalysts derived from bio-based materials to replace traditional rare or precious metals, addressing resource scarcity and cost challenges.
Green chemistry initiatives are driving the development of catalysts for carbon capture and utilization, enabling the conversion of CO₂ into valuable chemicals and fuels. Electrocatalysts for hydrogen production and storage are at the forefront of innovations in clean energy. Furthermore, AI and machine learning are accelerating the discovery and optimization of novel catalysts, reducing the time and cost associated with their development.
Advancements in 3D printing and additive manufacturing are enabling the precise design and scaling of catalysts tailored for specific industrial processes. Meanwhile, industry and academia are collaborating to develop circular catalytic systems that can be recycled and reused, aligning with the goals of a circular economy. As regulations tighten and industries aim for net-zero emissions, catalysts will play a pivotal role in enabling sustainable and efficient chemical manufacturing processes. This combination of innovation, digitalization, and sustainability promises a future where catalysts drive both economic and environmental benefits for the chemical industry.