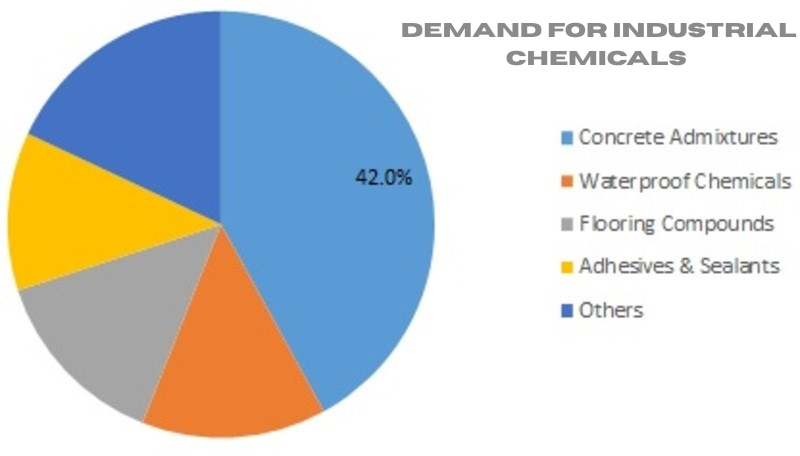
The construction industry is a major driver of demand for industrial chemicals, as these chemicals play a critical role in enhancing the performance, durability, and sustainability of construction materials. From concrete additives to advanced coatings, industrial chemicals are essential for modern construction projects. Here’s how the construction industry is driving demand for industrial chemicals:
1. Growth in Infrastructure and Urbanization
- Global Infrastructure Projects:
- Massive infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies, increases demand for construction chemicals.
- Examples:
- Highways, bridges, airports, and urban transit systems require specialized materials for durability and performance.
- Urbanization and Housing Demand:
- The rise in urban population drives the need for residential and commercial buildings, boosting the use of construction chemicals.
2. Demand for High-Performance Concrete
- Concrete Admixtures:
- Chemicals that enhance the properties of concrete, such as strength, workability, and setting time.
- Types:
- Plasticizers and superplasticizers for improved flow and reduced water content.
- Accelerators and retarders for setting time control.
- Air-entraining agents for freeze-thaw resistance.
- Impact:
- Essential for high-rise buildings, infrastructure projects, and extreme weather conditions.
3. Energy-Efficient Building Materials
- Thermal Insulation:
- Chemicals are used in the production of insulation materials to improve energy efficiency in buildings.
- Examples:
- Polyurethane foams for walls and roofing.
- Expanded polystyrene (EPS) for lightweight insulation panels.
- Cool Roof Coatings:
- Reflective coatings reduce heat absorption, lowering cooling costs.
4. Advanced Coatings and Sealants
- Protective Coatings:
- Used to protect structures from environmental damage, such as corrosion, UV rays, and moisture.
- Examples:
- Epoxy and polyurethane coatings for steel structures.
- Anti-corrosion coatings for bridges and marine infrastructure.
- Waterproofing Chemicals:
- Sealants and membranes prevent water infiltration in basements, roofs, and tunnels.
- Examples:
- Bitumen-based sealants for roofing.
- Silicone-based waterproofing for facades and joints.
5. Sustainable and Green Building Materials
- Low-VOC Adhesives and Coatings:
- Demand for eco-friendly products that comply with green building certifications like LEED.
- Recycled and Bio-Based Materials:
- Chemicals derived from renewable sources are used in sustainable construction practices.
- Examples:
- Bio-based polyols in insulation foams.
- Recycled polymers for composite building panels.
6. Flooring and Surface Treatments
- Epoxy and Polyurethane Flooring:
- Durable, chemical-resistant flooring solutions for industrial and commercial buildings.
- Surface Hardeners:
- Chemicals that enhance abrasion resistance and longevity of concrete floors.
- Decorative Coatings:
- Polymers and pigments for decorative finishes in residential and commercial spaces.
7. Adhesives and Bonding Agents
- Structural Adhesives:
- High-strength adhesives for bonding different materials, replacing traditional fasteners.
- Examples:
- Epoxy adhesives for pre-cast concrete.
- Polyurethane adhesives for composite panels.
- Tile Adhesives:
- Specialized adhesives for installing tiles on floors and walls.
8. Fireproofing and Safety
- Fire-Resistant Chemicals:
- Used in coatings, insulation, and construction materials to enhance fire resistance.
- Examples:
- Intumescent coatings for structural steel.
- Halogen-free flame retardants in composite panels.
- Impact:
- Essential for compliance with safety regulations in high-rise buildings and public infrastructure.
9. Lightweight and High-Strength Materials
- Polymer-Based Composites:
- Used for lightweight, durable components in modern construction.
- Examples:
- Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) for bridges and facades.
- Foaming Agents:
- Used to create lightweight concrete for non-load-bearing applications.
10. Renovation and Retrofitting
- Repair Chemicals:
- Chemicals for structural repair and rehabilitation of aging infrastructure and buildings.
- Examples:
- Epoxy injections for crack sealing.
- Corrosion inhibitors for reinforced concrete.
- Demand Drivers:
- Increased focus on extending the lifespan of existing structures drives the demand for specialized repair chemicals.
11. Regional and Global Trends
- Emerging Markets:
- Rapid construction in Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa drives demand for construction chemicals.
- Sustainability Regulations:
- Europe and North America focus on sustainable and energy-efficient construction, increasing demand for green chemicals.
- Mega Projects:
- Large-scale projects like smart cities, renewable energy installations, and transportation hubs contribute significantly to demand.
12. Innovations in Construction Chemicals
- Self-Healing Concrete:
- Incorporates chemicals that react with water to repair cracks autonomously.
- Nanotechnology:
- Nano-additives enhance the mechanical and thermal properties of construction materials.
- Example: Nano-silica for improved concrete durability.
- 3D Printing Materials:
- Specialized chemicals for 3D printing of construction components and structures.
13. Challenges and Opportunities
- Environmental Impact:
- Reducing the carbon footprint of construction chemicals remains a challenge.
- Opportunity: Development of low-emission and recyclable materials.
- Cost Management:
- High-performance chemicals often come at a higher cost.
- Solution: Improved efficiency and economies of scale in production.
Conclusion
The construction industry’s demand for industrial chemicals continues to grow as projects become more prominent, more complex, and environmentally conscious. From advanced concrete admixtures to sustainable coatings, industrial chemicals are integral to modern construction practices. Innovations in green chemistry and innovative materials will further shape this sector, aligning with global trends in urbanization, infrastructure development, and sustainability.
Hashtags
#ConstructionChemicals #IndustrialChemicals #ChemicalsInConstruction #BuildingWithChemistry #ConstructionMaterialsDemand #ConstructionDemand #ChemicalMarketGrowth #BuildingMaterialTrends #IndustrialGrowthDrivers #ConstructionIndustryTrends #ConcreteAdditives #WaterproofingSolutions #SealantsAndAdhesives #InsulationMaterials #SustainableConstruction #GreenBuildingMaterials #EcoFriendlyConstruction #SustainableChemicals #LowCarbonConstruction #InnovativeBuildingSolutions #SmartConstructionMaterials #ChemicalInnovation