Specialty chemicals play a crucial role in driving innovation across various industries, including electronics and healthcare, by enabling the development of advanced materials, products, and technologies. Their unique properties, tailored formulations, and high-performance characteristics allow them to meet the specific needs of these industries, driving advancements and improving performance. Here’s how specialty chemicals contribute to innovation in these two sectors:
1. Specialty Chemicals in Electronics:
The electronics industry relies heavily on specialty chemicals for manufacturing everything from semiconductors and displays to printed circuit boards (PCBs) and advanced coatings. These chemicals enable the development of new electronic devices with better performance, smaller sizes, and increased energy efficiency.
Key Contributions:
- Semiconductors and Microelectronics:
- Specialty chemicals, such as photoresists and etching agents, are used in the production of semiconductors. These chemicals help in creating the fine patterns needed in integrated circuits (ICs), enabling faster and more efficient microprocessors and memory devices.
- Advanced Lithography: High-performance photoresists are essential for photolithography, a process used to create smaller and more complex semiconductor circuits. This drives the miniaturization of electronic devices, allowing for more powerful processors in smaller form factors.
- Conductive Materials:
- Conductive Polymers: These specialty chemicals are used in flexible and lightweight electronics, such as flexible displays, touchscreens, and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). They provide conductivity while maintaining flexibility, leading to innovations in wearable devices, foldable screens, and flexible electronics.
- Metallic Inks: Conductive inks containing silver or copper nanoparticles are used in printed electronics, such as sensors, antennas, and RFID tags. These inks allow for the cost-effective production of electronic components on flexible substrates.
- Batteries and Energy Storage:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Specialty chemicals are crucial in the development of advanced battery technologies. Electrolytes, binders, and conductive materials improve the efficiency, energy density, and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries, which power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs).
- Solid-State Batteries: In the search for safer and higher-capacity batteries, specialty chemicals are used in the development of solid-state battery technologies. These batteries offer enhanced performance and safety compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries.
- Display Technologies:
- OLEDs and LCDs: Specialty chemicals are involved in the production of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and liquid crystal displays (LCDs). They are used as emissive materials, coatings, and solvents that enable high-resolution, energy-efficient, and flexible displays in devices like TVs, smartphones, and wearables.
- Protective Coatings:
- Anti-reflective Coatings: Specialty coatings are applied to electronic devices to reduce glare and enhance visibility, improving the user experience for screens and lenses.
- Corrosion-resistant Coatings: In electronics, especially in automotive and aerospace applications, specialty coatings are used to protect sensitive components from moisture, chemicals, and heat, ensuring long-term durability.
2. Specialty Chemicals in Healthcare:
In the healthcare sector, specialty chemicals are essential for the development of new drugs, medical devices, diagnostic tools, and treatments. Their role in enhancing the effectiveness, safety, and precision of healthcare products contributes significantly to medical innovation.
Key Contributions:
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs): Specialty chemicals are involved in the synthesis of APIs, which are the core ingredients in drugs. Innovations in chemistry have led to the creation of more effective and targeted medications for conditions like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Specialty chemicals are used to develop advanced drug delivery systems, such as liposomes, nanoparticles, and micelles, that improve the bioavailability, targeting, and controlled release of medications. These innovations ensure that drugs reach their intended site of action in the body, improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects.
- Biologics and Biopharmaceuticals: Specialty chemicals are integral in the development of biologic drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies and gene therapies, which are used to treat complex diseases like autoimmune disorders and certain cancers.
- Medical Devices and Implants:
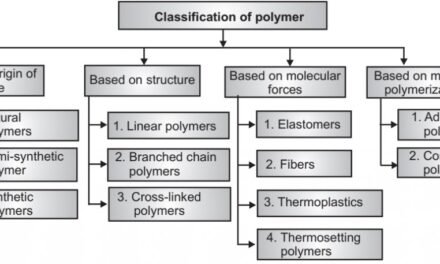
- Biocompatible Polymers: Specialty polymers are used in the production of medical devices such as catheters, stents, and pacemakers. These polymers are designed to be biocompatible, reducing the risk of rejection or adverse reactions when implanted in the body.
- Smart Devices: Innovations in specialty chemicals contribute to the development of “smart” medical devices that can monitor and manage health conditions in real-time. For example, chemical sensors and biosensors embedded in wearable devices can measure glucose levels, detect infections, or monitor blood pressure.
- Diagnostics:
- Diagnostic Reagents: Specialty chemicals are used in diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging agents, and in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) kits. They enable the detection of specific biomarkers, pathogens, or genetic material, improving the accuracy of medical diagnoses.
- Contrast Agents: Specialty chemicals are used in imaging procedures, such as MRI and CT scans, to enhance the contrast between tissues and improve the clarity of medical images. This leads to better diagnostic accuracy, especially in detecting cancers and neurological disorders.
- Personal Care and Cosmetics:
- Cosmetic Formulations: Specialty chemicals are essential in developing advanced skincare, haircare, and cosmetic products. They include moisturizers, anti-aging agents, sunscreens, and colorants that improve the health and appearance of the skin and hair.
- Controlled Release Systems: In cosmetics, specialty chemicals enable the development of controlled release formulations that provide long-lasting effects, such as time-released moisturizers or anti-aging compounds.
- Sterilization and Disinfection:
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants: Specialty chemicals are used in sterilization processes for medical equipment and in the formulation of antiseptics and disinfectants. These chemicals help prevent infections, particularly in hospital settings, ensuring patient safety.
- Surface Coatings: Specialty chemicals are used to create antimicrobial coatings for medical equipment, hospital surfaces, and personal protective equipment (PPE), reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs).