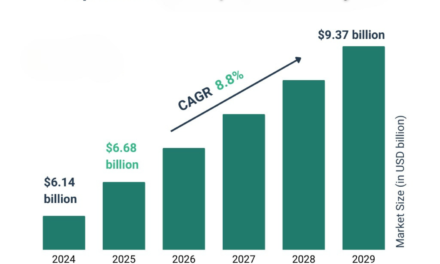
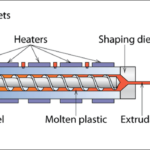
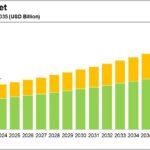
Specialty chemicals are critical enablers of green technologies, contributing to sustainability by improving energy efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and supporting the development of eco-friendly products and processes. From renewable energy systems to biodegradable materials, specialty chemicals play a vital role in advancing green technologies across various industries. Here’s how:
1. Renewable Energy
- Solar Panels:
- Materials for High Efficiency:
- Specialty chemicals like silicon precursors and anti-reflective coatings enhance the performance of photovoltaic cells.
- Examples: Trichlorosilane for silicon wafers and low-VOC coatings for durability.
- Encapsulation:
- Specialty adhesives and sealants protect solar panels from moisture and UV degradation.
- Materials for High Efficiency:
- Wind Turbines:
- Lightweight Composites:
- Specialty chemicals enable the production of epoxy and polyurethane resins for durable, lightweight wind turbine blades.
- Corrosion Protection:
- Anti-corrosion coatings protect offshore wind installations from harsh environments.
- Lightweight Composites:
- Energy Storage:
- Battery Technologies:
- Specialty chemicals are key to developing lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, ensuring high energy density and longer lifespans.
- Examples: Electrolytes like lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF₆) and advanced separators.
- Battery Technologies:
2. Green Building Materials
- Low-VOC and Sustainable Coatings:
- Specialty chemicals reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in paints and coatings.
- Examples: Waterborne and bio-based formulations for eco-friendly construction materials.
- Energy-Efficient Insulation:
- Advanced polymers like polyurethane foams improve thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption in buildings.
- Self-Healing Concrete:
- Specialty additives like microencapsulated healing agents repair cracks autonomously, extending infrastructure lifespan.
3. Biodegradable and Bio-Based Plastics
- Development of Biopolymers:
- Specialty chemicals facilitate the production of biodegradable plastics derived from renewable resources.
- Examples:
- Polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) for packaging and medical applications.
- Catalysts and Additives:
- Catalysts for efficient polymerization and additives for enhanced performance of bio-based plastics.
- Recyclability Enhancements:
- Specialty chemicals improve the recyclability of conventional plastics, enabling circular economy practices.
4. Water Treatment and Conservation
- Advanced Filtration Membranes:
- Specialty chemicals enable the production of high-performance reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment.
- Examples: Polyamide and polyethersulfone polymers.
- Green Disinfectants:
- Non-toxic biocides and oxidants for water purification reduce reliance on chlorine and other harmful chemicals.
- Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors:
- Chemicals prevent scaling and corrosion in industrial water systems, improving efficiency and reducing resource waste.
5. Biofuels and Green Energy
- Feedstock Processing:
- Specialty enzymes and catalysts improve the conversion of biomass into biofuels.
- Examples:
- Cellulase for breaking down lignocellulose and transesterification catalysts for biodiesel production.
- Improved Fuel Performance:
- Specialty additives enhance biofuel stability, combustion efficiency, and emissions profiles.
6. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- Absorption Materials:
- Specialty amines and ionic liquids capture CO₂ from industrial emissions efficiently.
- Examples: Monoethanolamine (MEA) and advanced solvents for post-combustion CO₂ capture.
- Mineralization Additives:
- Chemicals facilitate the conversion of captured CO₂ into stable carbonates for long-term storage or reuse.
7. Sustainable Agriculture
- Bio-Based Fertilizers:
- Specialty chemicals enable the production of controlled-release fertilizers and bio-based alternatives to reduce nitrogen runoff.
- Crop Protection:
- Eco-friendly pesticides and biostimulants derived from specialty chemicals minimize environmental impact.
- Examples: Neem oil-based formulations and microbial inoculants.
8. Green Manufacturing Processes
- Eco-Friendly Solvents:
- Specialty chemicals replace traditional solvents with biodegradable, non-toxic alternatives.
- Examples: Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and bioethanol as green solvents.
- Catalysts for Efficiency:
- High-performance catalysts reduce energy requirements and waste in industrial chemical processes.
- Examples: Zeolites and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for green catalysis.
9. Sustainable Textiles and Coatings
- Bio-Based Fibers:
- Specialty chemicals are used to produce eco-friendly fibers like lyocell and bio-polyester.
- Low-Impact Dyes:
- Specialty dyes reduce water and energy usage in textile manufacturing.
- Smart Coatings:
- Self-cleaning and water-repellent coatings reduce the need for detergents and frequent washing.
10. Green Cleaning Solutions
- Biodegradable Surfactants:
- Specialty surfactants enhance the cleaning power of detergents while being environmentally safe.
- Examples: Alkyl polyglucosides (APGs) derived from natural sugars.
- Eco-Friendly Disinfectants:
- Specialty chemicals replace harsh disinfectants with plant-based or bio-derived alternatives.
11. Challenges and Opportunities
- Cost of Development:
- High R&D costs for specialty chemicals tailored to green technologies.
- Opportunity: Increased regulatory support and consumer demand for sustainable products drive investments.
- Performance vs. Sustainability:
- Balancing the performance of green chemicals with environmental benefits.
- Opportunity: Advances in biotechnology and green chemistry are narrowing this gap.
12. Future Trends
- Circular Economy Integration:
- Specialty chemicals are enabling closed-loop systems, such as converting waste plastics back into raw materials.
- Green Hydrogen:
- Specialty chemicals like electrolytes and catalysts play a pivotal role in green hydrogen production and fuel cells.
- Innovative and Responsive Materials:
- Development of materials that adapt to environmental conditions for energy savings and efficiency.
Conclusion
Specialty chemicals are at the forefront of enabling and accelerating green technologies. By driving innovation in renewable energy, sustainable manufacturing, and eco-friendly materials, these chemicals play a pivotal role in addressing global environmental challenges and supporting the transition to a sustainable economy. As the demand for greener solutions grows, the specialty chemicals industry will continue to be a cornerstone of technological and environmental progress.
Hashtags
#SpecialtyChemicals #ChemicalsForGreenTech #GreenTechnologies #EcoInnovation #SustainableChemistry #ChemicalsInRenewables #BatteryChemistry #SolarTechMaterials #HydrogenEconomy #EnergyStorageInnovation #SustainableSolutions #CircularChemicals #GreenIndustrialProcesses #EcoFriendlyChemicals #LowCarbonTechnologies #TechForSustainability #InnovativeMaterials #SmartGreenTech #AdvancedChemistry #NextGenGreenTech #GreenTechMarket #SustainableIndustryTrends #FutureOfGreenTech #GlobalSustainabilityTrends #MarketForGreenSolutions