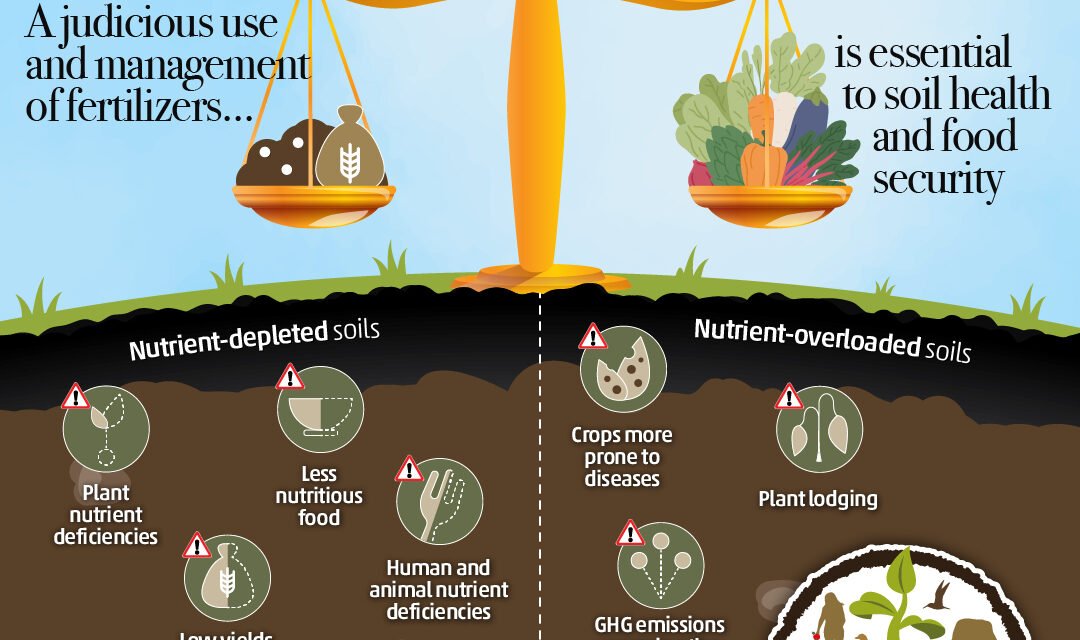
Fertilizers play a critical role in addressing global food security challenges by enhancing crop productivity, improving soil fertility, and enabling sustainable agricultural practices. As the global population grows and environmental constraints intensify, fertilizers are becoming increasingly essential for meeting the rising demand for food. Here’s an in-depth analysis of how fertilizers contribute to global food security:
1. Boosting Crop Yields
- Increased Productivity:
- Fertilizers supply essential nutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are vital for plant growth and higher yields.
- Example:
- Nitrogen fertilizers enhance photosynthesis and protein synthesis, critical for staple crops like wheat, rice, and maize.
- Role in Intensification:
- Fertilizers allow farmers to produce more on existing agricultural land, reducing the need for deforestation and expansion into fragile ecosystems.
2. Addressing Soil Nutrient Deficiencies
- Replenishing Depleted Soils:
- Continuous cropping and poor land management deplete soil nutrients; fertilizers restore these to maintain productivity.
- Site-Specific Nutrient Management:
- Precision agriculture tools guide the application of fertilizers tailored to specific soil and crop needs, improving nutrient use efficiency.
3. Supporting Smallholder Farmers
- Access to Fertilizers:
- Subsidy programs and initiatives ensure small-scale farmers in developing regions can access affordable fertilizers.
- Example:
- Programs like the African Fertilizer Financing Mechanism (AFFM) aim to increase fertilizer use in sub-Saharan Africa, where application rates are among the lowest globally.
- Empowering Productivity:
- Fertilizers help smallholder farmers maximize yields on limited land, ensuring food for their families and surplus for markets.
4. Enhancing Nutritional Quality
- Fortification with Micronutrients:
- Fertilizers enriched with micronutrients like zinc, iodine, and selenium improve the nutritional content of crops, addressing malnutrition.
- Example:
- Zinc-enriched fertilizers are used to combat zinc deficiency in populations relying on cereal-based diets.
5. Mitigating Climate Change Impacts
- Stress Tolerance:
- Fertilizers support plant resilience against drought, heat, and other climate-related stresses, ensuring stable yields.
- Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizers (EEFs):
- EEFs reduce nutrient losses through leaching and volatilization, minimizing environmental impact and improving resource efficiency.
6. Supporting Sustainable Farming Practices
- Integration with Organic Farming:
- Fertilizers complement organic amendments, improving nutrient availability and supporting regenerative agriculture.
- Precision Agriculture:
- Fertilizers integrated with precision tools optimize input use, reduce waste, and lower environmental impact.
- Crop Rotation and Intercropping:
- Fertilizers enhance the success of sustainable practices like crop rotation and intercropping, improving soil health and productivity.
7. Reducing Post-Harvest Losses
- Improved Crop Quality:
- Fertilizers promote uniform growth and enhance the shelf life of fruits, vegetables, and grains, reducing post-harvest losses.
- Supply Chain Impact:
- Higher-quality produce ensures better market access and reduced waste.
8. Regional Focus on Food Security
- Asia-Pacific:
- Fertilizers are essential for meeting the high food demand in densely populated countries like India and China.
- Sub-Saharan Africa:
- Fertilizer use is increasing to address chronic food insecurity and low agricultural productivity.
- Latin America:
- Expanding fertilizer use supports cash crop production, contributing to local food supply and global exports.
9. Addressing Emerging Challenges
- Growing Population:
- Fertilizers help farmers meet the food needs of a global population projected to reach 10 billion by 2050.
- Land Scarcity:
- Fertilizers maximize yields on limited arable land, preventing the need for agricultural expansion into ecologically sensitive areas.
- Soil Degradation:
- Nutrient replenishment with fertilizers combats soil degradation, ensuring long-term agricultural productivity.
10. Innovations in Fertilizer Technology
- Biofertilizers:
- Leveraging nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi to improve soil fertility sustainably.
- Controlled-Release Fertilizers:
- Gradual nutrient release aligns with crop uptake, improving efficiency and reducing losses.
- Smart Fertilizers:
- IoT-enabled fertilizers provide real-time nutrient release based on soil and crop conditions.
11. Collaboration and Policy Support
- Public-Private Partnerships:
- Collaboration between governments, international organizations, and private companies ensures fertilizer access and promotes sustainable use.
- Subsidies and Incentives:
- Targeted subsidies make fertilizers affordable for farmers in food-insecure regions.
- Capacity Building:
- Farmer training programs educate on proper fertilizer application techniques, reducing waste and improving outcomes.
12. Environmental Considerations
- Balanced Fertilizer Use:
- Proper nutrient management prevents overapplication, reducing risks of soil degradation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon-Neutral Production:
- Advancements in green ammonia production are reducing the carbon footprint of nitrogen fertilizers.
13. Future Outlook
- Scaling Sustainable Practices:
- Increased adoption of sustainable fertilizer practices will balance productivity with environmental stewardship.
- Focus on Marginal Lands:
- Fertilizers will be essential for making marginal lands productive, addressing regional food security gaps.
- Innovative Policies:
- Governments will need to align fertilizer policies with food security goals and climate adaptation strategies.
Conclusion
Fertilizers are indispensable for addressing global food security challenges by enhancing crop yields, improving nutritional quality, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices. With continued innovation and policy support, fertilizers will play a central role in ensuring a resilient and secure global food system for a growing population, while minimizing environmental impacts and adapting to climate change.
Hashtags
#GlobalFoodSecurity #FertilizersForFood #FoodSecuritySolutions #AgriForSecurity #FeedingTheWorld #SustainableAgriculture #EcoFriendlyFertilizers #ClimateSmartAgriculture #SustainableAgricultureGoals #GreenFertilizers #BoostingCropYields #HealthySoilsHealthyCrops #EfficientFertilization #SoilHealthMatters #NutrientRichFarming #AgriTechForSecurity #SmartFertilizers #PrecisionFarming #FertilizerInnovation #AdvancedAgriculture