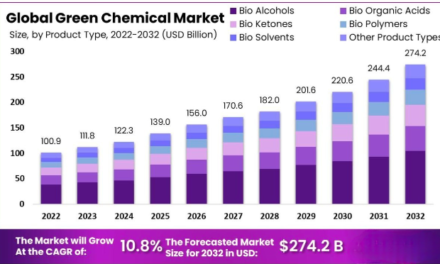
Specialty coatings are transforming the aerospace industry by enhancing performance, durability, and safety while addressing environmental and economic challenges. These advanced coatings are specifically engineered to meet the demanding requirements of aerospace applications, including extreme temperatures, high speeds, and exposure to harsh environments. Here’s how specialty coatings are advancing the aerospace industry:
1. Enhancing Corrosion Resistance
- Protection Against Environmental Factors:
- Aerospace components are exposed to humidity, salt spray, and atmospheric pollutants, leading to corrosion. Specialty coatings protect against these factors.
- Examples:
- Chrome-free corrosion-resistant coatings for aluminum and magnesium alloys.
- Epoxy-based primers with anti-corrosion properties.
- Longevity and Maintenance:
- Reduced corrosion extends the lifespan of aircraft components, lowering maintenance costs and downtime.
2. Thermal Management
- Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs):
- Protect engine components and exhaust systems from extreme temperatures, improving efficiency and durability.
- Examples:
- Ceramic-based TBCs for turbine blades and combustion chambers.
- Heat Dissipation Coatings:
- Coatings that manage heat distribution, preventing overheating of critical systems.
- Applications:
- Electronics, avionics, and structural components.
3. Weight Reduction
- Lightweight Coatings:
- Specialty coatings contribute to weight reduction by replacing heavier materials without compromising performance.
- Examples:
- Thin-film coatings and advanced polymers that reduce the need for heavy protective layers.
- Impact on Fuel Efficiency:
- Lower aircraft weight translates to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
4. Improving Aerodynamics
- Drag-Reducing Coatings:
- Specialty coatings minimize surface roughness, reducing drag and enhancing fuel efficiency.
- Examples:
- Fluoropolymer-based coatings for smooth airflow over wings and fuselage.
- Ice-Phobic Coatings:
- Prevent ice formation on critical surfaces like wings and engine inlets, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Examples:
- Hydrophobic and superhydrophobic coatings.
5. Extreme Weather Resistance
- UV Protection:
- Coatings protect exterior surfaces from UV radiation, preventing material degradation and color fading.
- Rain and Debris Erosion Resistance:
- Specialized coatings protect leading edges and rotor blades from erosion caused by rain, sand, and debris at high speeds.
- Examples:
- Polyurethane-based erosion-resistant coatings.
6. Fire Protection and Safety
- Intumescent Coatings:
- Expand under heat to provide fire resistance, protecting critical components and structural integrity.
- Applications:
- Passenger cabins, fuel tanks, and cargo holds.
- Flame Retardant Coatings:
- Minimize fire risk and comply with stringent safety regulations.
- Examples:
- Halogen-free flame retardants for interior surfaces.
7. Wear and Abrasion Resistance
- Hard Coatings:
- Enhance durability by resisting wear, scratches, and abrasion on landing gear, engine parts, and fasteners.
- Examples:
- Diamond-like carbon (DLC) and tungsten carbide coatings.
- Self-Lubricating Coatings:
- Reduce friction and wear in moving parts, improving reliability and extending service life.
8. Advanced Functional Coatings
- Anti-Reflective Coatings:
- Improve visibility and reduce glare on cockpit windows, instrument panels, and optical sensors.
- Radar-Absorbing Coatings:
- Reduce radar signature for military aircraft, enhancing stealth capabilities.
- Examples:
- Carbon-based and ferrite-based radar-absorbing materials.
9. Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
- Low-VOC and Chrome-Free Coatings:
- Specialty coatings comply with environmental regulations by reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and eliminating hexavalent chromium.
- Applications:
- Primers, topcoats, and corrosion-resistant systems.
- Durable Finishes:
- Long-lasting coatings reduce the need for frequent repainting, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
10. Advanced Application Techniques
- Self-Healing Coatings:
- Repair minor damages and scratches autonomously, extending the lifespan of coatings and underlying materials.
- Examples:
- Microcapsule-based self-healing polymers.
- Smart Coatings:
- Provide real-time data on wear, corrosion, or environmental exposure.
- Applications:
- Sensors embedded in coatings for structural health monitoring.
11. Aerospace Interior Enhancements
- Anti-Microbial Coatings:
- Prevent the growth of bacteria and viruses on interior surfaces, enhancing passenger safety and hygiene.
- Applications:
- Seat fabrics, tray tables, and lavatory surfaces.
- Decorative and Aesthetic Coatings:
- Provide durable finishes for a visually appealing cabin interior while maintaining performance.
12. Military and Space Applications
- High-Temperature Coatings:
- Protect components in hypersonic and re-entry vehicles exposed to extreme thermal and mechanical stresses.
- Radiation Shielding:
- Specialty coatings shield spacecraft and satellites from cosmic radiation and UV exposure.
- Abrasion-Resistant Coatings:
- Used on space equipment to withstand micrometeoroid impacts.
13. Economic and Operational Benefits
- Reduced Maintenance Costs:
- Durable coatings minimize wear, corrosion, and damage, reducing maintenance intervals and costs.
- Improved Aircraft Downtime:
- Quick-drying and long-lasting coatings ensure faster turnaround times for repairs and repainting.
Future Trends in Aerospace Specialty Coatings
- Nanotechnology:
- Nano-coatings offer improved thermal, mechanical, and anti-icing properties.
- Green Coatings:
- Increased focus on bio-based and waterborne coatings for environmental sustainability.
- 3D Printing Compatibility:
- Coatings designed for additive manufacturing applications in aerospace components.
- Intelligent Coatings:
- Advanced coatings with embedded sensors for predictive maintenance and real-time performance monitoring.
Conclusion
Specialty coatings are indispensable to the aerospace industry, enhancing performance, safety, and sustainability while reducing operational costs. As advancements in materials science and environmental regulations continue to shape the industry, specialty coatings will play a pivotal role in addressing future challenges and driving innovation in aerospace technology.
Hashtags
#SpecialtyCoatings #AerospaceCoatings #AdvancedMaterials #InnovativeCoatings #HighPerformanceCoatings #AerospaceIndustryImpact #AerospaceInnovation #AviationTechnology #FutureOfAerospace #AerospaceMaterials #NextGenAerospaceApplications #CorrosionProtection #ThermalBarrierCoatings #LightweightMaterials #DurableCoatings #FuelEfficiencySolutions #GreenAerospaceCoatings #EcoFriendlyCoatings #SustainableAerospace #TechnologyAndSustainability