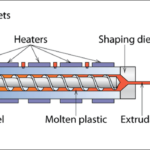
Additives are substances incorporated into plastics and polymers during their production or processing to enhance or modify the material’s properties. These additives can improve performance, durability, processing ease, or aesthetics, making plastics and polymers more suitable for a wide range of applications.
Types of Additives and Their Roles
- Plasticizers
- Purpose: Increase the flexibility and workability of plastics by lowering their glass transition temperature (Tg).
- Common Examples: Phthalates, adipates, and benzoates.
- Applications: Used in PVC (polyvinyl chloride) to make flexible products like cables, flooring, and medical tubing.
- Stabilizers
- Purpose: Prevent degradation of plastics during processing and use, such as thermal degradation or UV degradation.
- Types:
- Antioxidants: Prevent oxidation and preserve polymer integrity at high temperatures.
- UV Stabilizers: Protect plastics from UV radiation that causes degradation and discoloration.
- Common Examples: Hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), benzotriazoles.
- Applications: Polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC products exposed to sunlight.
- Flame Retardants
- Purpose: Reduce the flammability of plastics by inhibiting or delaying ignition.
- Common Examples: Brominated compounds, phosphorus-based compounds, and antimony trioxide.
- Applications: Electrical cables, upholstery fabrics, and construction materials.
- Colorants
- Purpose: Add color to plastics for aesthetic or functional reasons.
- Types: Dyes (which dissolve into the polymer matrix) and pigments (which are suspended particles).
- Common Examples: Titanium dioxide (white pigment), carbon black (black pigment), and azo dyes.
- Applications: Toys, automotive parts, packaging, and consumer goods.
- Fillers
- Purpose: Enhance the mechanical properties, reduce cost, and improve processability.
- Types:
- Inorganic fillers: Such as glass fibers, talc, and clay.
- Organic fillers: Such as wood flour and carbon black.
- Applications: Polypropylene and polyethylene composites, automotive parts, and construction materials.
- Benefits: Improve strength, stiffness, and heat resistance.
- Impact Modifiers
- Purpose: Improve the impact resistance and toughness of brittle plastics.
- Common Examples: Acrylic rubber, butadiene rubber, and EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer).
- Applications: Polystyrene, acrylics, and PVC used in products exposed to mechanical stress.
- Antistatic Agents
- Purpose: Reduce static charge buildup on plastics, which can attract dust and dirt, or cause electrical discharge.
- Common Examples: Quaternary ammonium compounds, carbon black.
- Applications: Electronics packaging, medical devices, and film products.
- Antimicrobial Additives
- Purpose: Prevent the growth of bacteria, fungi, and mold on plastic surfaces.
- Common Examples: Silver ions, zinc pyrithione, copper-based compounds.
- Applications: Medical devices, food packaging, and consumer products such as kitchenware.
- Processing Aids
- Purpose: Improve the ease of processing plastics during manufacturing, such as extrusion, molding, or compounding.
- Common Examples: Stearates (e.g., calcium stearate, zinc stearate).
- Applications: Used in the production of PVC, polypropylene, and polyethylene.
- Blowing Agents
- Purpose: Generate gas to create foam or expand the plastic during molding.
- Common Examples: Azodicarbonamide, sodium bicarbonate.
- Applications: Polyurethane foam, expanded polystyrene (EPS) used in packaging and insulation.
How Additives Enhance the Properties of Plastics
- Mechanical Properties
- Fillers like glass fibers and talc increase strength, stiffness, and impact resistance of plastics, making them suitable for structural and heavy-duty applications.
- Thermal and UV Stability
- Stabilizers, including antioxidants and UV protectants, improve the heat resistance and weatherability of plastics, making them ideal for outdoor or high-temperature environments.
- Durability
- Impact modifiers enhance toughness and prevent cracking or breaking under stress, improving the longevity of the material in demanding applications.
- Flammability Resistance
- Flame retardants enhance fire resistance, making plastics safer in applications like electrical cables, furniture, and automobiles.
- Processing Efficiency
- Processing aids facilitate easier molding and extrusion, reducing processing time and energy requirements during manufacturing.
- Aesthetic Appeal
- Colorants and surface enhancers provide desired colors, effects, or textures, increasing the product’s visual appeal and marketability.
- Functional Properties
- Antistatic agents and antimicrobial additives provide additional functionalities that are essential in applications like electronics packaging or healthcare products.
- Environmental Benefits
- Biodegradable additives can be incorporated into polymers to promote more eco-friendly disposal options, contributing to sustainability goals.