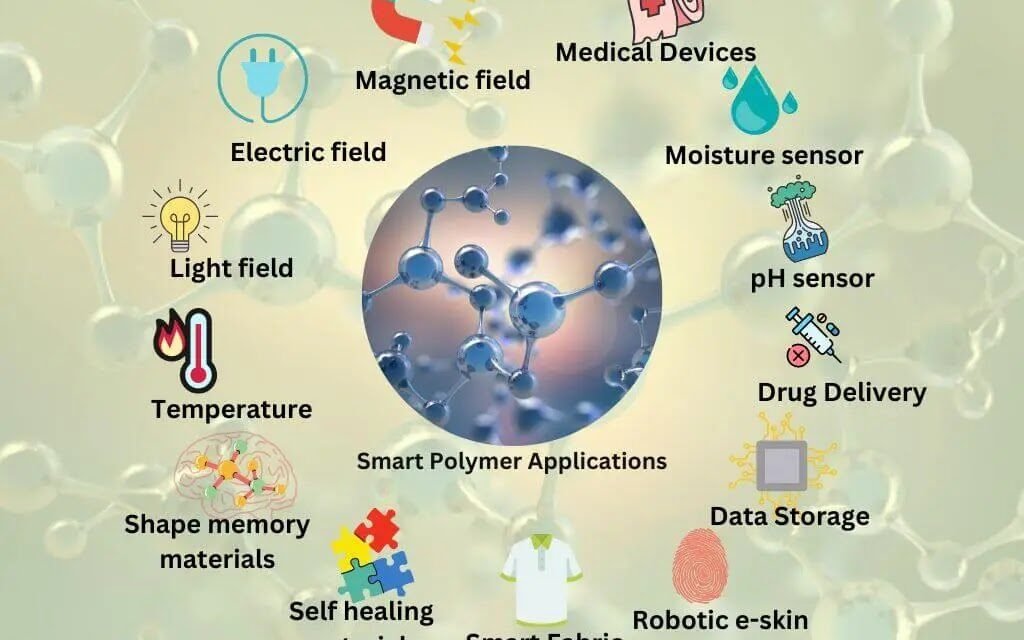
Polymers are being increasingly used in the development of smart materials and sensors due to their versatility and ability to respond to environmental stimuli. Below are key ways in which polymers contribute to the development of these advanced technologies:
1. Conductive Polymers in Sensors
- Polymers like polypyrrole and polyaniline can conduct electricity and change their electrical properties in response to stimuli such as light, temperature, or chemicals.
- Applications: Used in sensors for detecting gases, humidity, and bio-molecules, they provide real-time data conversion from environmental stimuli into electrical signals.
2. Polymers in Flexible and Wearable Sensors
- Stretchable Conductive Polymers: Polymers like conductive elastomers and hydrogels are used in wearable sensors that conform to the skin, ideal for health monitoring devices such as biosensors.
- Applications: These sensors monitor heart rate, sweat composition, and temperature, offering real-time health tracking in a non-invasive manner.
3. Shape-Memory Polymers (SMPs)
- Responsive to External Stimuli: SMPs can change shape when exposed to triggers like heat or light. This behavior is useful in developing self-healing materials and actuators.
- Applications: Used in smart materials like medical devices or robotic systems, where the material needs to respond dynamically to external conditions.
4. Polymers for Chemical and Environmental Sensors
- Polymer Nanocomposites: By embedding nanoparticles like carbon nanotubes or graphene into polymers, the material can be made more sensitive to environmental changes.
- Applications: These composites are used in sensors for detecting gases, pollutants, and toxic substances, offering high sensitivity and fast response times.
5. Polymers in Self-Healing Materials
- Polymer-based Self-Healing: Polymers embedded with microcapsules or vascular networks can repair damage autonomously.
- Applications: Used in sensors and smart materials, these self-healing polymers ensure durability by automatically repairing damage, thus enhancing the sensor’s lifespan and reliability.
6. Polymers in Light-Responsive Materials
- Photoresponsive Polymers: Polymers can be designed to change properties when exposed to specific wavelengths of light (UV, visible).
- Applications: These materials are used in smart windows, light sensors, and adaptive coatings, which alter their transparency or structure based on light exposure.
7. Polymers in Energy Harvesting
- Piezoelectric Polymers: Certain polymers can convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. These are used in sensors that don’t rely on external power sources.
- Applications: Self-powered sensors that monitor environmental factors like vibrations or pressure, such as those used in structural health monitoring.
8. Polymers for Environmental Monitoring
- Polyelectrolytes and hydrogels are polymers that can respond to changes in environmental conditions like humidity, pH, or temperature.
- Applications: Used in chemical sensors and biosensors that detect environmental changes such as pollution levels, water quality, or temperature fluctuations.
Polymers are integral to developing smart materials and sensors, offering flexibility, responsiveness, and customization for a wide range of applications, from healthcare monitoring to environmental sensing.