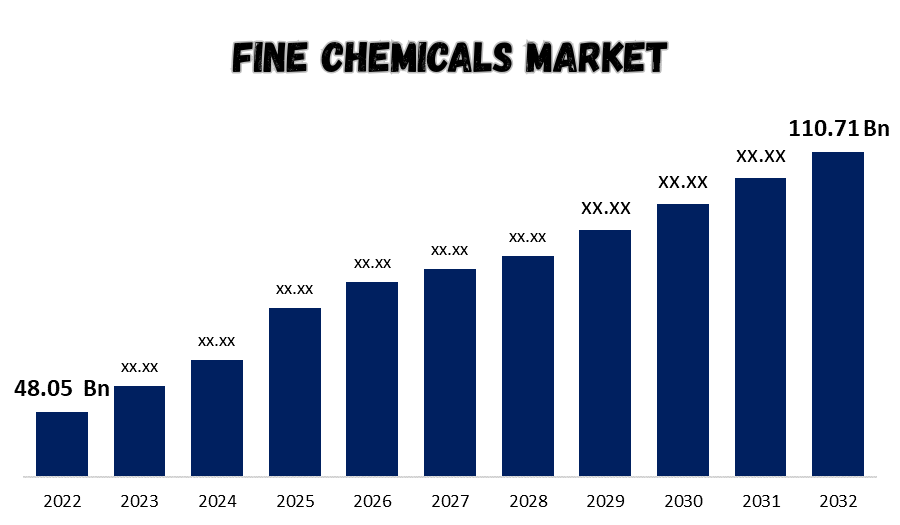
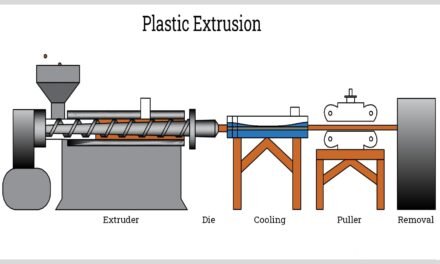
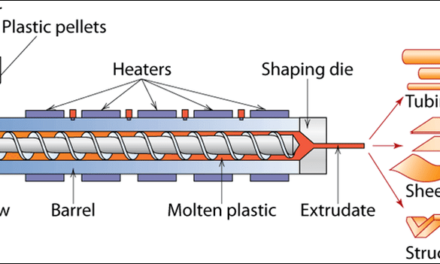
The fine chemicals market is highly responsive to shifts in global demand and regulatory standards, as these factors significantly influence production strategies, market dynamics, and the overall growth trajectory of the industry. Here’s how the market adapts to changes in demand and regulations:
1. Adapting to Shifts in Global Demand
- Market Diversification: Fine chemicals manufacturers often diversify their product lines to cater to different industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, agriculture, electronics, food additives) and geographic markets. When demand increases in one sector (e.g., healthcare or electronics), companies may prioritize production of those chemicals and adjust their supply chains accordingly.
- Customized Products: As global demand shifts, particularly towards specialty chemicals (e.g., for niche industries like biotechnology or green energy), manufacturers often respond by offering customized products that meet the specific needs of clients. Fine chemicals production is often tailored to customer specifications, allowing manufacturers to meet the evolving needs of the market.
- Innovation and R&D: In response to rising demand for new technologies or sustainability solutions, fine chemicals companies invest in research and development (R&D) to innovate and introduce new products. For example, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy has driven demand for fine chemicals used in batteries, solar cells, and advanced materials.
2. Responding to Regulatory Changes
- Compliance with Local and International Regulations: As regulatory standards change, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and food additives, manufacturers must adapt by ensuring that their products and processes comply with new and existing regulations. For example, the introduction of more stringent environmental regulations or health and safety standards requires manufacturers to implement green chemistry practices and adopt safer processes.
- Environmental Regulations: Regulations aimed at reducing the carbon footprint or controlling toxic emissions influence the production methods used in fine chemicals. In response, companies are increasingly turning to sustainable production practices, such as using renewable feedstocks, reducing waste generation, and implementing closed-loop systems for waste and water recycling.
3. Adjusting to Demand for Sustainable and Green Products
- Green Chemistry and Circular Economy: Regulatory changes favoring sustainability are driving demand for green chemicals and products with lower environmental impact. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting green chemistry principles, such as using renewable feedstocks, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste, to meet both consumer demand and regulatory pressure.
- Sustainable Packaging: In industries like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, regulatory demands for sustainable packaging are pushing manufacturers to explore biodegradable or recyclable materials for fine chemical products. This reflects a broader global demand for more environmentally responsible solutions across industries.
4. Agility in Production and Innovation
- Flexibility in Manufacturing: Fine chemicals producers must maintain flexibility in their manufacturing processes to respond quickly to shifts in both demand and regulatory requirements. This often involves modular or scalable production systems that allow companies to adjust output based on market conditions or regulatory shifts.
- Automation and Digitalization: The adoption of automation and digital tools like AI, big data, and machine learning allows manufacturers to improve production efficiency, enhance product quality, and monitor compliance with regulatory standards in real time. This enables companies to stay ahead of market trends and regulatory changes.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Fine chemicals manufacturers are increasingly collaborating with academia, research institutes, and regulatory bodies to stay ahead of technological developments and regulatory changes. These partnerships help to accelerate innovation in new products and processes that can better meet evolving global demands.
5. Navigating Supply Chain Challenges
- Raw Material Sourcing: Changes in regulatory standards, such as the introduction of restrictive legislation on certain chemicals, can disrupt supply chains and force manufacturers to find alternative raw materials or adapt their processes. Manufacturers respond by establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers and exploring new sourcing regions or materials that comply with evolving regulations.
- Global Trade and Tariffs: Shifts in global trade policies and tariffs can affect the supply and demand for fine chemicals. Manufacturers may need to adjust their supply chain strategies, potentially sourcing materials from new countries or finding ways to mitigate costs imposed by tariffs.
6. Proactive Market Intelligence and Forecasting
- Market Research: Manufacturers closely monitor market trends, regulatory changes, and consumer behavior to anticipate shifts in global demand. Through market intelligence and forecasting, they can adjust their production schedules, R&D efforts, and marketing strategies to stay competitive and meet evolving market needs.
By effectively adapting to shifts in global demand and regulatory standards, fine chemicals manufacturers are able to stay competitive, ensure compliance, and meet the evolving needs of industries across the world.