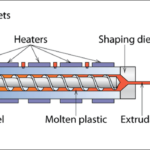
Recent research has raised concerns about the potential health risks associated with certain chemicals found in everyday consumer products, particularly their link to chest electrical alterations or disturbances in the electrical activity of the heart. Some chemicals, often used in personal care items, cleaning agents, and plastics, have been found to affect cardiac function and may contribute to the development of arrhythmias or other heart rhythm disorders.
One group of chemicals that have been scrutinized for their potential health effects are endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs). These include substances like phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), and certain flame retardants. EDCs can interfere with the body’s hormonal system and have been shown to impact the regulation of heart function. Studies suggest that prolonged exposure to EDCs, even in low doses, could influence the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate and rhythm, leading to altered electrical signals in the heart.
Another class of chemicals under investigation are volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are commonly found in cleaning products, paints, and air fresheners. Some VOCs, such as formaldehyde and toluene, can be inhaled or absorbed through the skin, and there is evidence suggesting that exposure to these chemicals may have toxic effects on cardiovascular health. High levels of VOCs may lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are linked to arrhythmias and other heart disorders.
Heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, found in various consumer goods, including certain cosmetics and older electronic devices, are also linked to adverse effects on the heart. These metals can accumulate in the body over time, disrupting normal heart function and increasing the risk of electrical disturbances in the chest. Lead poisoning, for instance, has been associated with hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias.
The risk of chest electrical alterations due to chemicals in consumer products is exacerbated by cumulative exposure. Many individuals are regularly exposed to a combination of these harmful substances, often without being aware of their presence in everyday items. This long-term exposure could increase the likelihood of developing cardiac issues over time, particularly in individuals who are genetically predisposed to heart conditions.
Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have been working to establish stricter guidelines on the use of certain chemicals in consumer products. Efforts to phase out or limit the use of known toxic substances like BPA and phthalates in consumer goods are ongoing, with some manufacturers opting for safer alternatives. Consumer awareness campaigns are also helping to educate the public about potential risks, prompting individuals to make more informed choices when purchasing household items.
There is growing evidence that certain chemicals in everyday products can interfere with the electrical activity of the heart, leading to disturbances like arrhythmias. The ongoing research into these connections aims to raise awareness, improve safety standards, and reduce exposure to potentially harmful substances that may affect cardiac health.