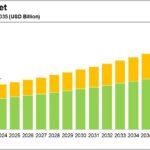
The future of agrochemicals in sustainable farming is being shaped by innovative approaches aimed at reducing environmental impact while maintaining agricultural productivity. Key developments include the integration of nanotechnology, the adoption of biofertilizers, and the advancement of green ammonia production.
Nanotechnology offers promising solutions for enhancing the efficiency of agrochemicals. Nano-fertilizers, for instance, provide nutrients to crops precisely when needed, minimizing runoff and waste. This targeted delivery improves nutrient uptake and reduces the frequency of applications, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
Biofertilizers, which utilize living microorganisms to enrich soil fertility, are gaining traction as eco-friendly substitutes for synthetic fertilizers. They enhance nutrient availability, promote plant growth, and mitigate environmental concerns associated with chemical fertilizers. The continuous use of biofertilizers has been shown to improve soil health and support sustainable agriculture.
Traditional ammonia production for fertilizers is energy-intensive and a significant source of carbon emissions. Innovations in green ammonia production, utilizing renewable energy sources, are emerging to address this issue. For example, companies like TalusAg are developing solar-powered systems to produce green ammonia, aiming to reduce carbon footprints and enhance food security, particularly in regions like sub-Saharan Africa.
These advancements reflect a broader commitment within the agricultural sector to adopt sustainable practices. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and eco-friendly alternatives, the future of agrochemicals is poised to support farming methods that are both productive and environmentally responsible.