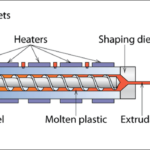
In recent years, the collaboration between academia and industry has grown significantly, particularly in sectors like chemical manufacturing, biotechnology, and materials science. These partnerships are fueling innovation and advancing scientific research while addressing real-world challenges. Several success stories highlight how academia and industry working together can yield transformative results:
BASF and the University of Heidelberg: Advancing Sustainable Chemistry
One of the most prominent collaborations in the chemical industry is between BASF, a global leader in chemicals, and the University of Heidelberg in Germany. Their partnership focuses on advancing sustainable chemistry and green technologies. The collaboration has led to the development of novel catalysts that improve the efficiency of chemical reactions and reduce energy consumption in industrial processes. This partnership is also exploring renewable energy solutions and sustainable materials, helping BASF achieve its sustainability goals while contributing to cutting-edge research. The outcome of this collaboration has had significant implications for improving production processes across the chemical industry.
MIT and Dow Chemical: Innovations in Advanced Materials
The partnership between MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) and Dow Chemical exemplifies how academic-industry collaborations drive breakthroughs in advanced materials. Through their ongoing efforts, the team has worked on developing new polymers and composite materials with superior properties, including enhanced strength, lightness, and resistance to heat. These innovations are paving the way for the development of materials used in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. The collaboration has led to tangible results, such as new material formulations for the automotive industry that improve energy efficiency and safety.
Imperial College London and Johnson Matthey: Catalysis Research
Johnson Matthey, a global leader in sustainable technologies, has collaborated extensively with Imperial College London in the field of catalysis. Their research partnership has led to the development of advanced catalytic processes that improve the production of cleaner chemicals and fuels, contributing to a more sustainable chemical industry. This collaboration has also focused on reducing the environmental impact of industrial manufacturing through the development of green catalysts and more efficient processes. As a result, Johnson Matthey has been able to integrate the research findings into their commercial products, advancing their role in promoting sustainability.
University of Cambridge and Syngenta: Agricultural Innovations
The collaboration between the University of Cambridge and Syngenta, a global leader in agricultural science, has led to major advancements in crop protection and food security. Researchers from Cambridge have worked with Syngenta to explore the genetic and molecular mechanisms behind plant resilience to disease and environmental stress. This partnership has led to the development of more effective and environmentally friendly pesticides, as well as innovations in seed treatments that boost crop yield. The success of this collaboration has helped Syngenta strengthen its position in sustainable agriculture and contributed to global efforts to address food security.
Stanford University and Tesla: Electric Vehicle Battery Research
Stanford University has been collaborating with Tesla on a range of research initiatives, particularly in the development of advanced electric vehicle (EV) battery technologies. This collaboration has led to advancements in lithium-ion battery efficiency, energy density, and sustainability. The work done at Stanford’s labs has been crucial in pushing the boundaries of battery performance, helping Tesla reduce production costs and improve the range and efficiency of its EVs. As the demand for electric vehicles grows, the academic-industry partnership between Stanford and Tesla is driving critical innovations that are reshaping the automotive industry.
University of California, Berkeley and BASF: Bio-based Materials
The collaboration between BASF and the University of California, Berkeley focuses on bio-based materials and renewable chemistry. The two entities are working together to develop polymers derived from plant-based feedstocks, which can replace petroleum-based plastics in various applications. The partnership aims to advance the commercialization of bio-based products, reduce environmental impact, and create new business opportunities in sustainable materials. This collaboration has already resulted in the development of bio-based polyurethanes, which are now being tested for use in automotive and construction applications.
University of Manchester and Graphene@Manchester: Advancing Graphene Research
The University of Manchester has become a leader in graphene research, and their collaboration with industry partners, including major corporations like Samsung and Versarien, is revolutionizing the materials science sector. Graphene, a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon, has exceptional electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from electronics to medical devices. The University’s Graphene@Manchester initiative has fostered collaboration between academia and industry, leading to significant advances in graphene production, scalability, and application. These developments have set the stage for graphene to become a key material in industries like electronics, energy storage, and advanced manufacturing.
Oxford University and Pfizer: Drug Development
The partnership between Oxford University and Pfizer has been instrumental in the development of life-saving vaccines and treatments. One of the most notable collaborations was in the development of the COVID-19 vaccine. Pfizer and the university’s research teams worked together to accelerate the development of the vaccine, leveraging the university’s cutting-edge research in immunology and Pfizer’s expertise in vaccine manufacturing. The successful collaboration has highlighted the importance of academic-industry partnerships in addressing global health challenges.